GMP Annex 1 Implementation How Ready-To-Use Vials and Cartridges Can Meet New Regulation Requirements Efficiently

EU GMP Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products outlines the requirements for manufacturing sterile medicinal products in the EU (1). This article explores how the latest update to Annex 1 impacts the sterile medicine production supply chain and how ready-to-use (RTU) containers, such as vials and cartridges, offer a time-efficient and cost-effective solution for compliance.
Introduction and Key Trends in Sterile Manufacturing
Sterile manufacturing is a dynamic segment of the pharmaceutical industry, highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic's demand for a resilient supply chain. The market for sterile-manufactured drug products is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% from 2022 to 2027 (2), driven by biologics, biosimilars and personalized medicines. This growth necessitates increased production capacity, efficiency and quality while reducing complexity and waste.
However, expanding sterile capacity involves significant investment, long lead times and regulatory compliance challenges. New regulations often require costly equipment upgrades, such as restricted-access barrier systems (RABS) and isolators, which could increase the difficulty for smaller companies to implement.
The sterile manufacturing sector is evolving rapidly, driven by several key trends (3):
- Reduced total cost of ownership: Streamlined processes and improved yields reduce costs and increase efficiency
- Innovation in products and processes: New technologies and processes enhance manufacturing and distribution
- Industry convergence: Collaboration among stakeholders in drug development and manufacturing
- Competitive intensity: Small and medium-sized injectable personalized products require flexibility in production lines and workforce skills to optimize processes and reduce waste
Adapting to these trends is crucial for success in sterile manufacturing, with a focus on reducing lifecycle duration and demonstrating return on investment. Underserved regions drive growth in sterile manufacturing. Currently, over 80% of global capacity is in North America and Western Europe. However, drug shortages and patent expirations are pushing companies to expand in emerging markets, leveraging cost-effective technologies and capital investments. Local production is supported by rising living standards and government initiatives to strengthen internal supply chains.
Emerging economies in Asia, Eastern Europe, South America and Africa present significant growth opportunities. However, this requires substantial investment in new equipment and the revamping of existing lines, along with sufficient time for qualification and validation. Overcoming these barriers with innovative approaches is crucial for market success. Companies may need to partner with other stakeholders in the drug supply chain to balance the demand for flexible sterile capacity with cost and time constraints.
GMP Annex 1 Overview and Impact on Manufacturers
The revised Annex 1 introduces significant changes to sterile manufacturing, emphasizing pharmaceutical quality systems (PQS), quality risk management (QRM) and contamination control strategy (CCS). It also expands coverage for new technologies like isolators and RABS, while updating requirements on monitoring, disinfection and training.
Manufacturers must establish a comprehensive CCS to produce sterile products under compliant conditions. This involves implementing modern PQS elements and extensive use of QRM principles, as outlined in the International Council Harmonization (ICH) guidelines, specifically ICH Q9: Quality Risk Management and ICH Q10: Pharmaceutical Quality System (4). Ensuring compliance reduces the risk of contamination and ensures patient safety.
How Design Can Help Manufacturers Ensure Compliance
The new QRM updates require manufacturers to identify measures to mitigate potential risks in their processes. This involves comprehensively evaluating a facility's infrastructure, production processes, equipment design and primary packaging materials. The revised Annex 1 covers a wide range of sterile product types, including active substances, excipients, primary packaging materials and finished dosage forms. This reduces the need for extensive qualification and validation activities for primary containers, as contamination and sterility are managed by packaging producers with robust quality systems.
The importance of Annex 1 is underscored by numerous conferences and events focused on its implementation. A survey by the PDA revealed that many companies are not fully compliant with the new requirements. Most respondents were from the EU and North America, with a significant number still using RABS (5). The survey indicated that companies using open RABS must invest in more restricted barriers and reduce human intervention to comply with updated regulations (see Figures 1-3)
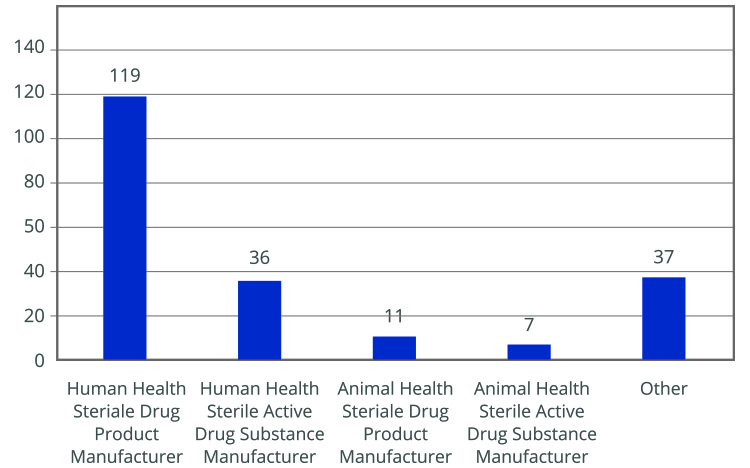
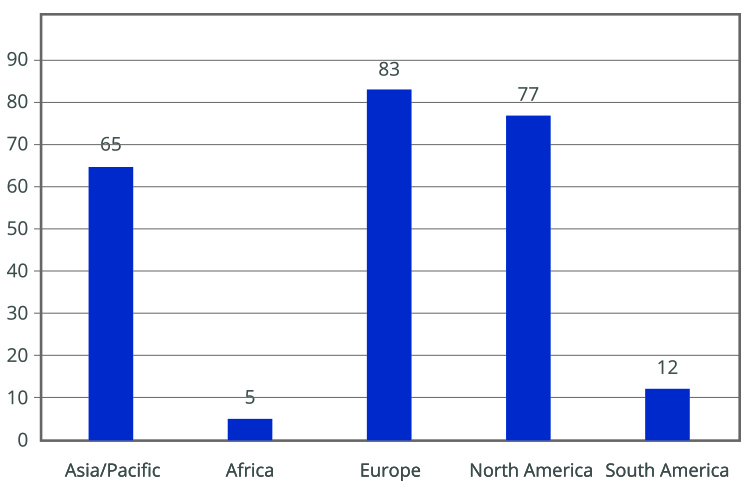
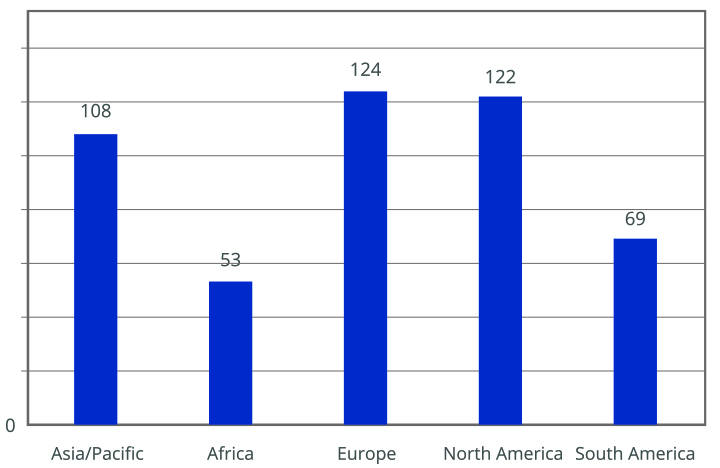
Key drivers for adopting new technologies include increased sterility assurance, reduced manufacturing costs and improved efficiency. However, these changes require significant economic investment and may lead to production interruptions. A practical solution to reduce execution times and costs is using sterile and RTU packaging. RTU packaging simplifies the filling process by eliminating steps such as washing, depyrogenation, drying and sterilization, which are typically required for preparing primary containers before filling. This approach enhances sterility assurance and operational efficiency while minimizing contamination risks.
Comparison of Traditional and RTU Processes
Comparing traditional and RTU processes highlights the efficiency of RTU components. RTU containers reduce complexity, cost and time while supporting quality and regulatory compliance. Key aspects include:
- Manual with Traditional Containers: Involves multiple steps and higher risk of contamination
- Semi-Automatic with Traditional Containers: Reduces some manual handling but still complex
- Automatic with RTU Containers: Streamlines processes, reduces handling and improves efficiency
RTU containers demonstrate superior efficiency by avoiding several production steps and reducing complexity and costs while enhancing process control and product quality to align with market and regulatory expectations. By analyzing each process step, we can highlight the following key aspects:
- Incoming Stage
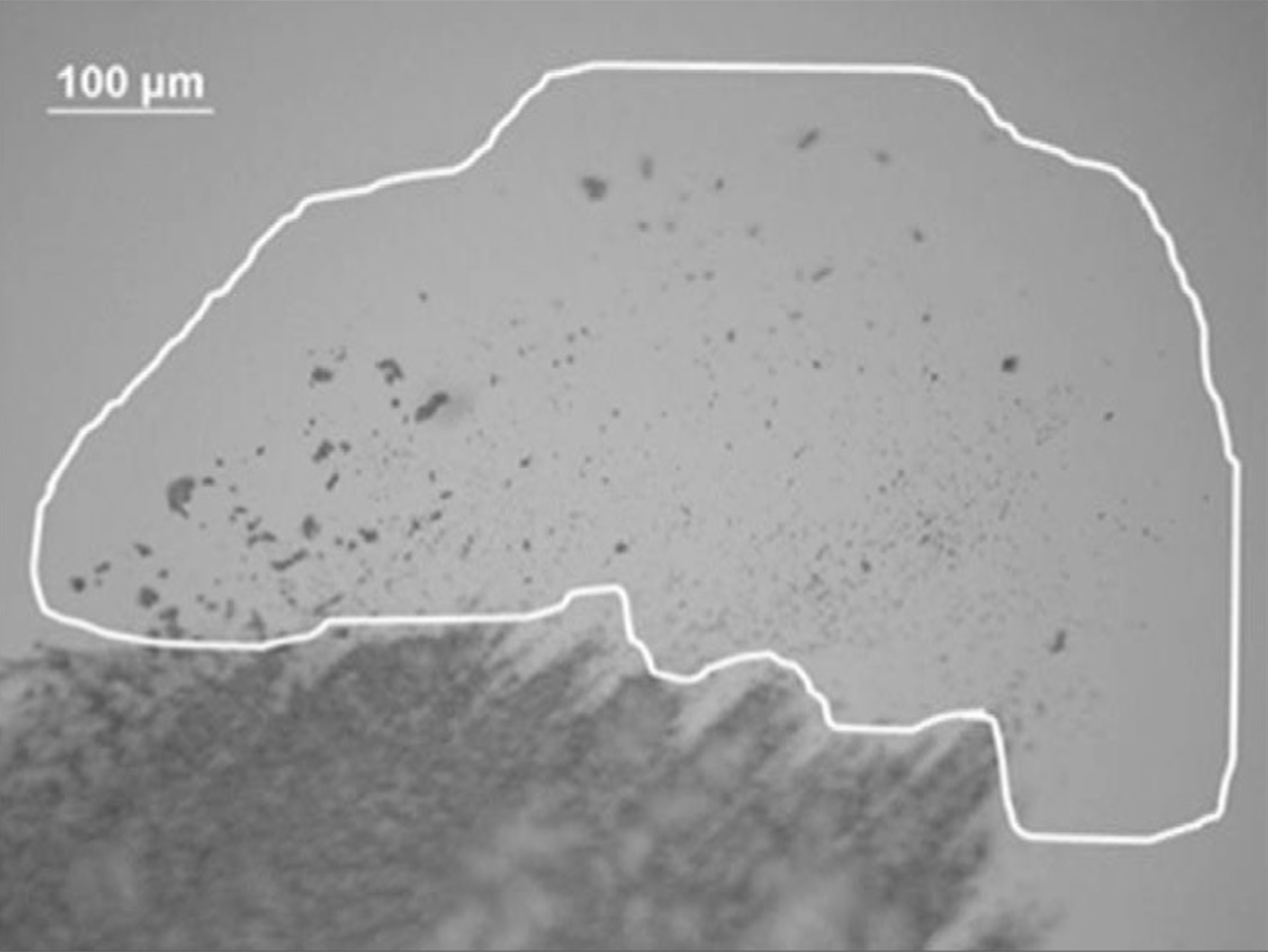
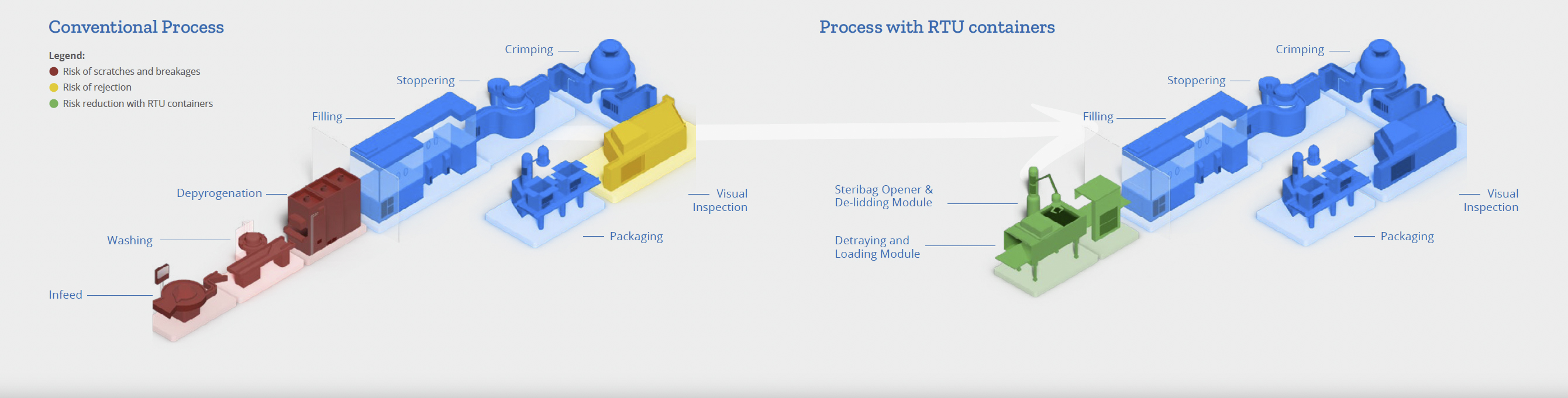
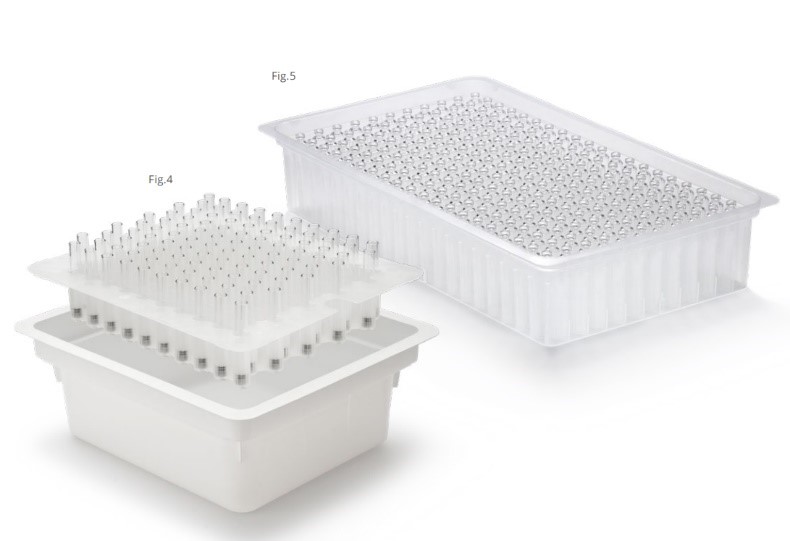
Traditional containers require extensive quality control testing and documentation review before release for filling, necessitating appropriate warehouse storage. In contrast, RTU containers arrive pre-washed and pre-sterilized in nest-and-tub or tray packaging, with cartridges well separated. This packaging prevents frictive sliding during transportation, reducing particle generation and the risk of scratches, which can lead to contamination and defects (see Figure 4).
- Washing and Depyrogenation
Standard containers need washing and depyrogenation before filling, involving significant handling and processing. This increases the risk of contamination and defects. Washing uses purified water, water for injection and pharma gases, with manual de-wrapping and feeding. Depyrogenation involves high temperatures, which can damage containers. RTU containers eliminate these steps, reducing handling and associated risks.
Operational and Quality Advantages of Using RTU Containers
RTU containers offer several operational advantages over traditional containers, particularly by eliminating manual processes involved in washing and depyrogenation, which can introduce inconsistencies, quality deviations and potential yield reductions (see Figure 5). Key Benefits of pharmaceutical companies choosing RTU containers are listed below (and quantified in Table 1):
- Reduction in production time
- Reduction in equipment involved
- Reduction in employees' resource
- Reduction in maintenance activities
- Reduction in validation and re-validation activities
- Reduction in inventory/stock of spare parts
- Reduction in environmental and process controls
- Reduction in risk of product defects generated by RTU containers helps mitigate contamination risks, a key goal under the revised Annex 1 requirements. They require less preparation in CCS due to fewer risky activities. RTU packaging suppliers must meet strict quality standards and provide documentation to ensure sterility.
The use of RTU containers offers several quality advantages to pharmaceutical companies, including the following:
- Less documentation and effort for qualification
- Minimal human intervention, reducing the risk of contamination
- Fewer activities needed for installation qualification, operational qualification performance qualification and process validation protocols
- Reduced risk of container contamination due to better packaging and handling
- Less aseptic manipulation and fewer process controls in Grade A areas
Overall, RTU containers improve efficiency, reduce contamination risks and enhance product quality by eliminating several manual, high-risk steps in the production proces (6).
Conclusion
Our market analysis highlights several key points:
- Rapid Growth and Challenges: The sterile pharma market is expanding quickly but presents significant challenges
- Need for Simplification: Reducing complexity is essential to enhance service levels
- Importance of Innovation: Innovation will be a crucial differentiator
- Collaboration is Key: Cooperation among supply chain stakeholders is vital to overcome challenges and seize market opportunities
The pharmaceutical market operates under strict regulations, requiring suppliers to be resilient and adaptable to new guidelines. The revised Annex I introduces key rules for sterile applications:
- Knowledge and Awareness: Understand your processes thoroughly
- Risk Management: Be aware of risks throughout the manufacturing process, including materials and suppliers
- Mitigation Strategies: Implement and document risk mitigation measures
- Partner Involvement: Collaborate with partners to adopt the best solutions
- Focus on Innovation: Use barrier technologies to minimize risks from human intervention
Implementing RTU primary packaging, like Stevanato Group’s EZ-fill® platform, offers significant benefits, enhancing sterility assurance, reducing operational risks and minimizing recalls (see Figure 6).
Under the revised Annex 1, a CCS is crucial for demonstrating compliance and mitigating risks to patient safety. RTU packaging is an effective solution for controlling contamination and reducing human intervention.
RTU materials also support manufacturers by reducing capital expenditure (CAPEX) through subcontracting washing and depyrogenation, allowing a focus on aseptic filling in restricted equipment (RABS or Isolator).
RTU primary packaging materials provide a robust solution to meet regulatory expectations and capitalize on market growth opportunities.

| STANDARD CONTAINERS | RTU CONTAINERS | Δ** | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Activities |
| Loading at the beginning of the filling machine; no washing and depyrogenation in line or in batch |
|
| Documentation Review associated with batch manufacturing |
| Quality Documentation review without washing and depyrogenation steps | 15%-20% Batch executed documentation review effort reduction |
| Quality |
| No deviation due to steps removed | Approx 2 deviations/week reduction per filling line including ΔP inversion deviation from the filling room Grade A and the cooling area of the tunnel which could call for additional cleaning activities during manufacturing. No related investigations and tests/environmental and personnel controls needed |
Results of Table 1 refer to the findings and conclusions derived from investigations or studies conducted by Giovanni Cosmi and Mirko Gabriele
References
- https://health.ec.europa.eu/medicinal-products/eudralex/eudralex-volume-4_en#annexes
- IQVIA, Alira Health; Data communicated during the Capital Markets Day, Sep. 27 2023
- Growth Opportunities in Sterile Injectable Outsourcing – Frost & Sullivan – June 2022
- https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines
- Survey-report---implementation-of-new-eu-annex-1-and-implementation-of-barrier-systems-16-aug-2023.pdf (pda.org) PDA Annex I Survey August 2023 (% values removed from the graphs)
- Advances in Vial Processing in Pharmaceutical Primary Packaging to Reduce Risk of Vial Damage and Particle Contamination - Pharmaceutical Processing World



